A Brief Overview
- When families and schools meet to discuss a student’s special education program, they can find Common Ground by remembering that everyone wants the student to receive a Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE).
- Two short videos, A Tale of Two Conversations, provide a quick look at how a meeting might feel like one long argument or a helpful collaboration. The difference starts with preparation and approach.
- Read on for tips about getting ready for a collaborative meeting.
- The Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) also provides information about parent and student rights.
- PAVE has prepared a Communications log sample for you to use.
Full Article
Whether on Zoom or around a conference table, sitting down with a team of professionals can feel intimidating to families. When a child’s Individualized Education Program (IEP) is on the agenda, emotions can overtake a meeting. Getting defensive or angry does not usually help, however. This article provides tools for staying organized, open minded, and on topic to improve the work of meetings—and student outcomes.
A basic special education vocabulary boosts empowerment, and empowered families generally feel more confident at their meetings. Here is a key word to know:
Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE)
A student with an IEP has the right to FAPE. That right is protected by federal law—the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). To meet the standard of FAPE, special education services are accessible to the student. Accessible means the services work as designed to enable progress appropriate, in light of the child’s circumstances.
A student receiving FAPE with appropriate, accessible services demonstrates steady progression toward mastery of skills. Those skills are being taught with specially designed instruction (SDI). As skills are learned, progress is measured through goal tracking. Meaningful progress indicates that the student is accessing FAPE.
Mastery can enable a sense of belonging. When the student feels capable, connected, and responsible within the school community, things generally run more smoothly for everyone.
In other words, FAPE is the result when everyone works together for the benefit of the student and meaningful learning happens. When a student is successful, the IEP team has done its job well and everyone can celebrate!
Here is a more formal way to talk about FAPE: Under the IDEA, FAPE requires an IEP reasonably calculated to provide progress appropriate, in light of the child’s circumstances.
FAPE provides a place to begin
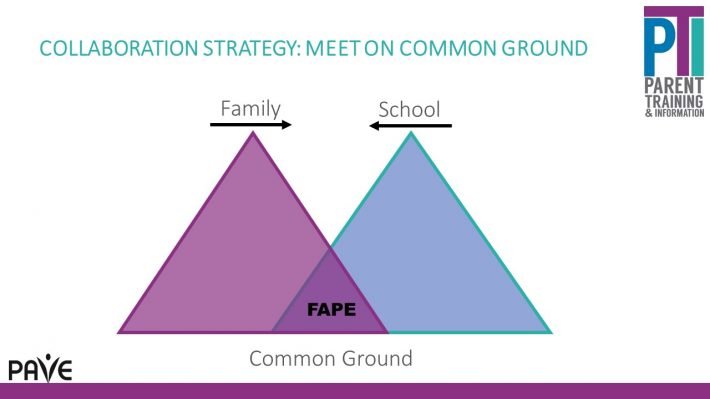
When families and schools meet to talk about a child’s services, everyone can begin with FAPE as the overarching goal. FAPE provides Common Ground for the discussion. Everyone on the team wants FAPE:
- The school district is required by law to provide FAPE to IEP-eligible students.
- Teachers are happy when their students are successful.
- The family wants a child to learn in a meaningful way.
- The student wants to feel confident and proud.
Common Ground is not always where meetings begin
Problems arise in meetings when school staff and/or family members start the conversation far from Common Ground. The Center for Appropriate Dispute Resolution in Special Education (CADRE) has designed a curriculum to support families and schools in their discussions. Two short videos, A Tale of Two Conversations, provide a quick look at how a meeting might feel like one long argument or a helpful collaboration. The difference starts with preparation and approach.
To avoid a meeting that feels like a fight, the parent may want to start the meeting with some general comments to help school staff better understand the student and to gently remind the team that years of parenting have led to some expertise about a specific child.
For example, an IEP or a behavior plan might say that a student is “defiant” or “refusing” to do work. Those types of statements can make a parent feel defensive. Showing up angry probably will not lead to a productive meeting. Instead, a parent may come to the meeting prepared to explain that the student lacks confidence and would rather appear defiant than “stupid.” Maybe the parent has been able to talk to the student about their frustrations and can bring statements or requests directly from the student.
Another way to find common ground is to prepare open-ended questions and bring those to the table first, before offering suggestions or requests. For example, if a parent shows up and demands a 1:1 right at the start of the meeting, the conversation might quickly devolve into an argument about resource problems. If a parent comes ready to talk about what is not working for the student and concerns for their child’s learning and well-being, there is an opportunity to build empathy and problem-solving.
Climb mountains as a team
Firm predetermined “solutions” from any side can position school staff and family members far from collaboration, like the peeks of two mountains unable to ever meet in the middle.
Consider collaborative problem-solving as a project that starts at the intersecting bases of two mountains, on Common Ground. Shared expectations and assumptions are a good place to begin for an open-minded discussion. Here are a few conversation starters to consider:
- According to these progress reports, the student is getting good at … How might we use that emerging skill to scaffold skill-building in this other area?
- My student is not making as much progress as I expected in this area… Can we talk about strategies for improving progress?
- This assignment, grade, or record shows that the student struggles to … Is there another approach to services or placement that we have not considered yet as a team?
- I notice that this IEP goal is written to help the student “stop” doing an unwanted behavior. Can you help me understand the skill that is being taught, and can we rewrite the goal to focus on measuring progress toward the expected skill or behavior?
- From what I see here (data/evidence/observations), this service is not working or is not accessible to the student. My theory about this is… Does anyone here have a different theory about what might be going on?
Here are some big-picture concepts for productive collaboration:
- Trust is at the heart of positive working relationships.
- Family members and educators can develop trust by showing personal regard, respect, transparency, and integrity. These may be particularly important for trust to grow among people of different cultures.
- Blaming, bringing up the past repeatedly, minimizing another’s opinion, or rushing a conversation can create barriers to collaboration.
- A neutral third party may be needed to resolve issues and rebuild relationships.
Prepare for the meeting
Request any documents that are going to be discussed at the meeting ahead of time. Review the documents in preparation for the meeting and mark down any notes for discussion. Whether meeting to discuss an IEP, a Section 504 Plan, behavior, ancillary services, or something else, families are better served when they prepare. To help families organize their concerns and requests, PAVE offers a format for designing a Handout for the Team Meeting. An alternative version supports self-advocates: Students: Get Ready to Participate in Your IEP Meeting with a Handout for the Team.
Leave with an action plan
At the end of the meeting, review what has been decided and be sure to make notes about any action steps, deadlines, or assignments. Be sure to note:
- What is the action?
- When will it happen?
- Who is responsible?
Schedule a follow-up conversation or a plan to communicate about anything that is not firmly decided. After a formal meeting, the school sends parents a Prior Written Notice (PWN) to describe any changes being made to a student’s services and when those changes will take effect. Parents with their own notes about the action plan will better understand how to read the PWN and whether there are unresolved topics.
Procedural Safeguards provide additional options
If a meeting leaves too many issues unresolved, parents can review their procedural safeguards to make a choice about what to do next. A copy is offered by the school at all formal meetings, and parents can also request a copy any time. The Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) also provides information about parent and student rights.
Parents have the right to disagree with the school and to pursue resolution by:
- Requesting mediation or a facilitated IEP meeting, which is a longer meeting with a third-party facilitator hired by the state (free to families).
- File a state complaint with OSPI.
- Requesting a due process hearing, perhaps with legal representation.