The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a federal law that was passed in 1990 and has been amended. The IDEA provides children with qualifying disabilities, from birth to age 21, with the right to services designed to meet their unique, individual needs.
A Brief Overview
- The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a federal law that entitles children to special education services if disability significantly impacts access to education and a specially designed program is needed.
- IDEA has been federal law since 1990, and key concepts are from the Education for All Handicapped Children Act, passed in 1975. PAVE provides an article and infographic about disability rights history.
- A primary principle of the IDEA is the right to FAPE (Free Appropriate Public Education) for students eligible for special education services. FAPE rights are also protected by civil rights laws, including Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973.
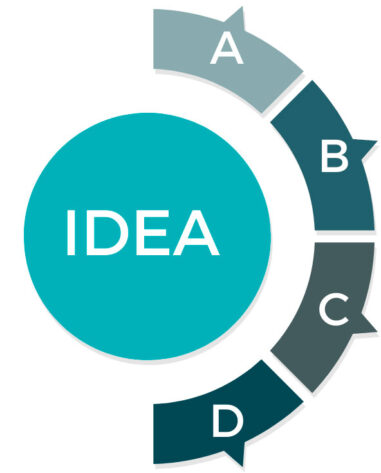
- IDEA consists of four parts that ensure that individuals with disabilities receive support and education throughout their lives, from early childhood through adulthood.
- To qualify for an IEP, a student meets criteria in one of the 14 eligibility categories (WAC 392-172A-01035), the disability must have a negative impact on their learning, and the student must require specially designed instruction (SDI) to benefit from the general education curriculum.
Introduction
Eligible children ages 3-21 who receive services at school have a right to FAPE: Free Appropriate Public Education. In accordance with the IDEA, FAPE is provided when individualized services enable a student with a disability to make progress that is appropriate, in light of their circumstances.
Services are delivered through an Individualized Education Program (IEP). A non-discriminatory evaluation and family participation on an IEP team are aspects of FAPE. Families have dispute resolution options that are described in the Procedural Safeguards.
IDEA requires FAPE to be provided in the Least Restrictive Environment to the maximum extent possible, which creates a responsibility for schools to serve students in the general education environment, with appropriately inclusive access to grade-level learning, whenever possible. Access to general education might be provided through an adapted curriculum, additional adult support, assistive technology, or something else. PAVE provides more information about Washington State’s work to improve inclusive practices.
Many of these concepts were part of IDEA’s predecessor law, the Education for All Handicapped Children Act, passed in 1975. That was the first United States law that required schools to provide special education services to all children with eligible disabilities. PAVE provides an article and infographic about disability rights history. The IDEA’s primary features are further detailed later in this article.
The IDEA drives how states design their own special education policies and procedures. Title 34, Part 104 is the non-discrimination federal statute under the Office for Civil Rights Department of Education. In Washington State, rules for the provision of special education are in Chapter 392-172A of the Washington Administrative Code (WAC).
FAPE is an important acronym to learn!
Families often ask: What does the school have to provide? The answer to that question is FAPE. The school district is responsible to make sure a student with an eligible disability condition is receiving FAPE.
As part of their right to FAPE, a student eligible for an IEP has the right to an individualized services program that ensures their education is appropriate, equitable, and accessible. All of those terms are part of FAPE. Figuring out how to provide FAPE is the work of an IEP team, and part of FAPE is ensuring that family is part of the decision-making team.
FAPE must ensure that the student finds meaningful success, in light of their circumstances. Trivial progress on IEP goals or the same goals year after year does not meet the federal standard for FAPE. A lawsuit referred to as Endrew F was settled by the 2017 U.S. Supreme Court and included specific requirements for meaningful progress and parent participation.
If a neighborhood school cannot provide the services and programming to guarantee FAPE within the general education classroom, then the school district is responsible to work through the IEP process to design an individualized program and placement that does meet the student’s needs. Keep in mind that Special Education is a Service, Not a Place: see PAVE’s article with that statement as its title.
IDEA considers the whole life of a person with a disability
IDEA includes Parts A, B and C. The right of a child with disabilities to receive an education that prepares that child for adult life is stated in Part A:
“Disability is a natural part of the human experience and in no way diminishes the right of individuals to participate in or contribute to society…
“Improving educational results for children with disabilities is an essential element of our national policy of ensuring equality of opportunity, full participation, independent living, and economic self-sufficiency for individuals with disabilities.”
Part B of the IDEA covers children ages 3 through 21—or until graduation from high school. Students who receive services through an Individualized Education Program (IEP) are covered under Part B.
Part C protects infants and toddlers, aged 0 (birth) to 3 years old, who need family support for early learning. The disability category of developmental delay overlaps early learning and IEP and can qualify a child for free, family-focused services to age 3 and school-based services through age 9. PAVE provides downloadable toolkits specifically designed for parents and families of young children:
- From Birth to Three Toolkit: This toolkit provides places to begin if caregivers suspect that a baby or young child may need services due to a developmental delay or disability.
- Transition Toolkit for Ages 3-5: This toolkit encompasses a collection of our informative articles, complemented by sample letters to provide you with a solid foundation as you navigate through this crucial transition period.
Part D outlines grants and funding for programs that help students with disabilities get a better education, including:
- Teacher training programs to train teachers and school staff in Washington State on the best ways to teach students with disabilities.
- Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI)’s Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) – a system that helps train school staff on how to support students’ academic, social, emotional, and behavioral needs.
- Parent Training and Information Centers help students with disabilities and their families understand their rights, navigate the special education process, and get involved in their children’s education. PAVE provides Parent Training and Information (PTI) to family caregivers, youth, and professionals in Washington state with questions about services for children and young people with disabilities, aged 0-26. In addition, Community Parent Resource Centers (CPRCs) serve the same function as PTIs but are typically smaller and located in underserved communities, often addressing the needs of families from culturally or linguistically diverse backgrounds. CPRC, Open Doors for Multicultural Families serves multicultural families in South King County.
- Educational technology funds can be used to buy or create technology that helps children with disabilities learn, so they have the same opportunities as other students.
- Transition services help students with disabilities move from high school to adult life, like getting a job, going to college, or living independently.
- Washington’s Early Support for Infants and Toddlers (ESIT), can use Part D funds to help research and expand services for young children with disabilities to get them ready for school.
Eligibility for school-based services
To qualify for an IEP, a student meets criteria in one of the 14 eligibility categories defined in WAC 392-172A-01035. The disability must have a negative impact on learning. Not every student who has a disability and receives an evaluation will qualify for an IEP. Following procedures described by the IDEA, school districts evaluate students to consider 3 key questions:
- Does the student have a disability?
- Does the disability adversely impact education?
- Does the student need Specially Designed Instruction (SDI)?
When each answer is yes, a student qualifies for services. In each area of identified need, Specially Designed Instruction (SDI) is recommended to help the student overcome the impact of the disability to access FAPE. Progress in that area of learning is tracked through goal-setting and progress monitoring.
Additional Information
- Special Education Blueprint: The Six Principles of IDEA
- Evaluations Part 1: Where to Start When a Student Needs Special Help at School
- Student Rights, IEP, Section 504 and More
- Steps to Read, Understand, and Develop an Initial IEP
- PAVE’s downloadable toolkits
PAVE provides training on a variety of topics, including live and on-demand, in person and online. Register for an upcoming training on the PAVE calendar.





















