New parents often worry about their child’s growth and development, especially when comparing with other children. Early intervention can be crucial for children with developmental delays or disabilities. In Washington, families can connect with a Family Resource Coordinator (FRC) for guidance and access free developmental screenings. The Department of Children, Youth and Families (DCYF) offers services through Early Support for Infants and Toddlers (ESIT), providing evaluations and individualized plans (IFSP) to support eligible children from birth to age three. These services, protected under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), are typically free and aim to help children thrive in various settings.
A Brief Overview
- PAVE provides downloadable toolkits specifically designed for parents and families of young children, including From Birth to Three Toolkit and Transition Toolkit for Ages 3-5.
- Families concerned about a child’s development can call the Family Health Hotline at 1-800-322-2588, with support in multiple languages. Parents can complete a free developmental screening online at Parent Help 123.
- Washington’s Department of Children, Youth and Families (DCYF) administers family-focused services for eligible children from birth to age 3 through Early Support for Infants and Toddlers (ESIT).
- The Individualized Family Service Plan (IFSP), funded by Part C of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, is a whole family plan developed with input from caregivers and professionals. It includes goals, services, and progress monitoring, and is reviewed regularly.
- To qualify, a parent must provide written permission for ESIT to conduct an early intervention evaluation of their child. If the evaluation results indicate that the child has a developmental delay or disability, ESIT will develop an IFSP. PAVE provides a Next Steps Checklist: When Your Child is Found Eligible for Early Intervention Services (EIS).
- Early intervention services (EIS) are designed to meet the child’s individual needs, including various therapies and support services. Services are typically provided in the child’s home or other natural environments.
- Various dispute resolution options are available, including mediation and due process. Parents can contact their ESIT Family Resource Coordinator (FRC) if they have concerns or disagreements.
- Most early intervention services are provided at no cost to families. Some services may be billed to insurance with family consent, but certain services are always free under IDEA.
- Active-duty servicemembers whose dependents receive EIS must enroll in the Exceptional Family Member Program (EFMP) for their branch, or the Coast Guard’s Special Needs Program (SNP).
Introduction
New parents may struggle to know whether their child’s growth and development are on track. They may have a feeling that a milestone is missed, or they may observe siblings or other children learning and developing differently. Sometimes a parent just needs reassurance. Other times, a child has a developmental delay or a disability. In those cases, early interventions can be critical to a child’s lifelong learning.
Seek guidance from a Family Resource Coordinator (FRC)
Washington families concerned about a young child’s development can call the Family Health Hotline at 1-800-322-2588 (TTY 1.800.833.6384) to connect with a Family Resource Coordinator (FRC). Support is provided in English, Spanish and other languages. Families can access developmental screening online for free at HelpMeGrow Washington.
Several state agencies collaborated to publish Early Learning and Development Guidelines. The booklet includes information about what children can do and learn at different stages of development, focused on birth through third grade. Families can purchase a hard copy of the guidelines from the State Department of Enterprise Services. A free downloadable version is available in English, Spanish, and Somali from DCYF’s Publication Library. Search by title: Washington State Early Learning and Development Guidelines, or publication number: EL_0015.
Washington early intervention services are provided by ESIT
In Washington, the Department of Children, Youth and Families (DCYF) administers services for eligible children from birth to age 3 through Early Support for Infants and Toddlers (ESIT). Families can contact ESIT directly, or they can reach out to their local school district to request an evaluation to determine eligibility and consider what support a child might need. The ESIT website includes videos to guide family caregivers and a collection of Parent Rights and Leadership resources, with multiple language options.
Early intervention services (EIS) are provided in the child’s “natural environment,” which includes home and community settings where children would be participating if they did not have a disability. According to ESIT, “Early intervention services are designed to enable children birth to 3 with developmental delays or disabilities to be active and successful during the early childhood years and in the future in a variety of settings—in their homes, in childcare, in preschool or school programs, and in their communities.”
Early services are delivered through an IFSP
Children who qualify receive services through an Individualized Family Service Plan (IFSP). The right to an IFSP is protected by Part C of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). The IDEA is a federal grant program that provides funding for states to implement early learning and special education programs. Part B of the IDEA protects an eligible school-age student’s right to an Individualized Education Program (IEP). Part A includes general guidance about the educational rights of children 0-22.
Family caregivers, childcare professionals, teachers, or anyone else can refer a child for an early learning evaluation if there is reason to suspect that a disability or developmental delay may be impacting the child’s growth and progress. The school district’s duty to seek out, evaluate and potentially serve infants, toddlers or school-aged students with known or suspected disabilities is guaranteed through the IDEA’s Child Find Mandate.
First Step: Evaluate to determine eligibility
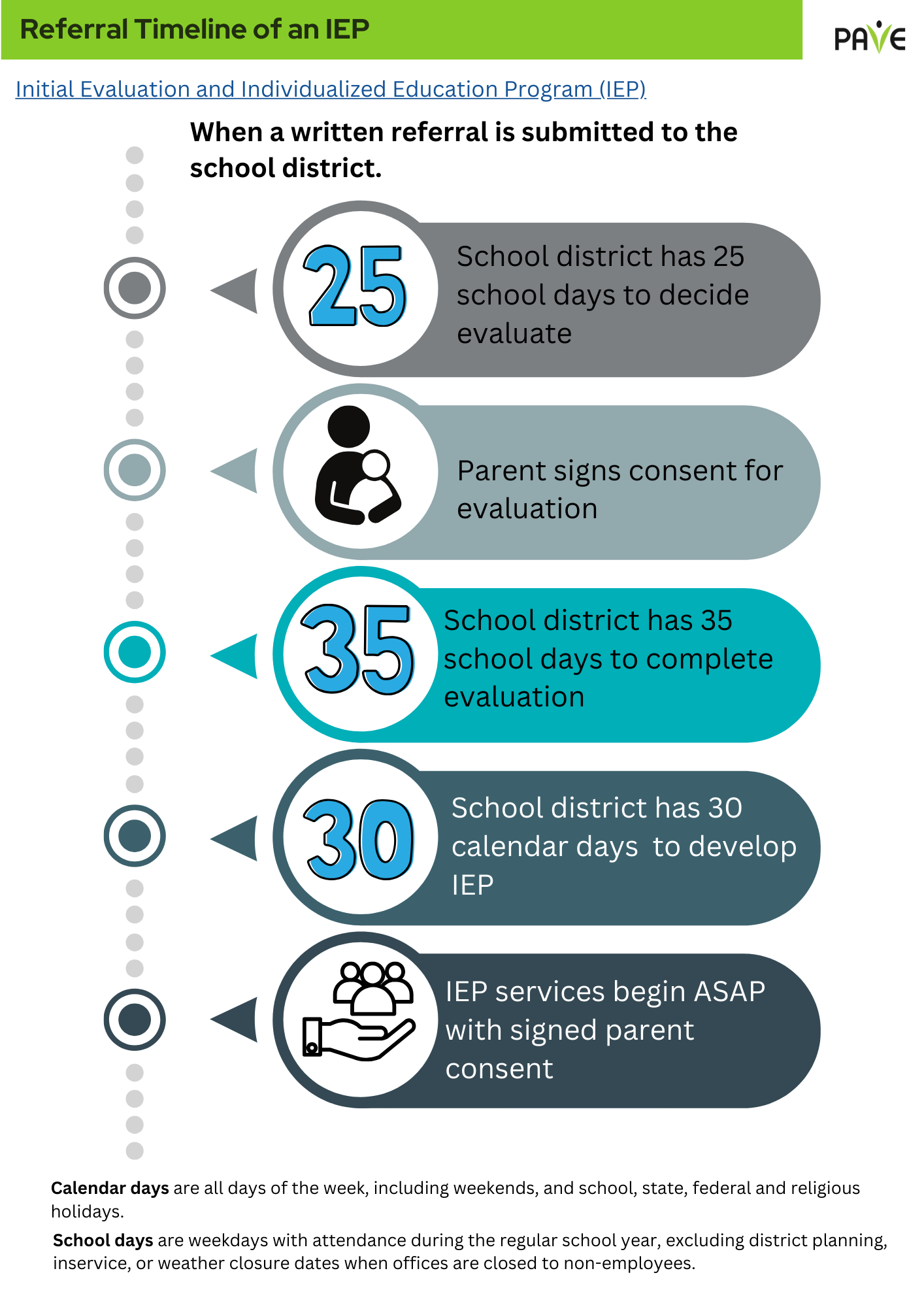
Early intervention is intended for infants and toddlers who have a developmental delay or disability. Eligibility is determined by evaluating the child (with parental consent) to see if the little one does, in fact, have a delay in development or a disability. Eligible children can receive early intervention services from birth to the third birthday. PAVE provides an article that describes What Happens During an Early Intervention Evaluation, and a checklist for When Your Child is Found Eligible for Early Intervention Services (EIS).
Next Step: Develop a service plan
If an infant or toddler is eligible, early intervention services are designed to meet the child’s individual needs. Options might include, but are not limited to:
- Assistive technology (devices a child might need)
- Audiology or hearing services
- Speech and language services
- Counseling and training for a family
- Medical services
- Nursing services
- Nutrition services
- Occupational therapy
- Physical therapy
- Psychological services
Services are typically provided in the child’s home or other natural environment, such as daycare. They also can be offered in a medical hospital, a clinic, a school, or another community space.
Individualized Family Service Plan (IFSP): What is the plan?
The IFSP is a whole family plan, with the child’s primary caregivers as major contributors to its development and implementation. Parents/custodial caregivers must provide written consent for services to begin. In Washington, Family Resource Coordinators (FRCs) help write the IFSP. Team members may include medical professionals, therapists, child development specialists, social workers, and others with knowledge of the child and recommendations to contribute.
The IFSP includes goals, and progress is monitored to determine whether the plan is supporting appropriate outcomes. The plan is reviewed every six months and is updated at least once a year but can be reviewed at any time by request of parents or other team members. The IFSP includes:
- The child’s current developmental levels and needs in physical, cognitive, communication, social/emotional, and adaptive areas
- Family information: resources, priorities, and concerns of parents/caregivers.
- Major results/outcomes expected from the child and family
- Specific services:
- Where services are provided—any services provided outside the child’s “natural environment” of home/daycare/community require a statement explaining the rationale for the placement
- When the child receives services—the number of days or sessions for each service, and how long each session will last
- Who pays for the services
- Name and contact information for the Family Resource coordinator (FRC) responsible for IFSP implementation
- Steps to begin at age 2.5 to support the child’s transition out of early intervention and perhaps into school-based services.
- If relevant, additional services or information for the family—such as financial guidance or parenting support
PAVE provides a downloadable checklist to help parents familiarize themselves with the IFSP.
Dispute resolution options are available
If parents have a concern or disagree with any part of the early intervention process, they can contact their Family Resource Coordinator (FRC). If issues remain unresolved, families may choose from a range of dispute resolution options that include mediation, due process, and more. ESIT provides access to a downloadable parent rights brochure with information about dispute resolution options in multiple languages.
Most services are free to families
Washington State provides most early intervention services at no cost to families of eligible children. Some services covered by insurance are billed to a child’s health insurance provider, with the signed consent of a family caregiver. The early intervention system may not use health care insurance (private or public) without express, written consent.
Part C of the IDEA requires states to provide the following services at no cost to families: Child Find (outreach and evaluation), assessments, IFSP development and review, and service coordination.
Early intervention services for military families
Military-connected infants and toddlers receiving early intervention services must be enrolled in the Exceptional Family Member Program (EFMP) while their servicemember is on active-duty orders. The Exceptional Family Member Program (EFMP) is a mandatory program for all branches of the U.S. Armed Forces that helps military dependents with special medical or educational needs. The Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Space Force each have an EFMP and the Coast Guard, which operates under the authority of the Department of Homeland Security, has a similar program called the Special Needs Program (SNP).
The Early Childhood Technical Assistance Center (ECTA), funded by the U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Special Education (OSEP), builds state and local capacity to improve outcomes for young children with disabilities and their families. Military-connected families and others relocating or living outside of Washington State can contact the early intervention services program in their new state with the help of ECTA’s Early Childhood Contacts by State directory.
Military families moving from or to installations that have Department of Defense Education Activity (DoDEA) schools will receive their early intervention services from Educational and Developmental Intervention Services (EDIS). Referrals may come to EDIS from any military medical provider or the parents. Upon receipt of a referral to EDIS, an initial service coordinator is assigned to contact and assist the Family. The initial service coordinator gathers information to understand the family’s concern, shares information about early intervention, and makes arrangements to proceed with the process. In EDIS, any member of the early intervention team can serve as an initial service coordinator. EDIS is provided in locations where DoDEA is responsible for educational services, including some installations on the eastern side of the United States.
Learn More
PAVE provides downloadable toolkits specifically designed for parents and families of young children:
- From Birth to Three Toolkit: This toolkit provides places to begin if caregivers suspect that a baby or young child may need services due to a developmental delay or disability.
- Transition Toolkit for Ages 3-5: This toolkit encompasses a collection of our informative articles, complemented by sample letters to provide you with a solid foundation as you navigate through this crucial transition period.
For additional information:
- The Learn the Signs. Act Early. website provides tools for tracking milestones and materials for families to learn more and plan home-based activities that promote skill development. “Early intervention services can change a child’s developmental path and improve outcomes for children, families, and communities,” the CDC encourages. “Help your child, help your family! Families benefit from early intervention by being able to better meet their children’s needs from an early age and throughout their lives.”
- Check the PAVE calendar for trainings and events, including the Starting Strong webinar about how IDEA supports the rights of infants and toddlers with developmental delays or disabilities and their families.
- PAVE provides an article for next steps after age 3: What’s Next when Early Childhood Services End at Age 3? Another PAVE article for families new to special education: Steps to Read, Understand, and Develop an Initial IEP.