With summer approaching, parents may worry about their child’s progress being disrupted. They can request a meeting with the IEP team to review progress and address concerns. Extended School Year (ESY) services are available to help maintain skills and prevent regression. ESY is individualized and can be provided during breaks or as an extension of the school day.
A Brief Overview
- Extended School Year (ESY) services help a student with a disability maintain skills in academic and/or functional areas, such as speech/language, occupational therapy, or behavior.
- The Individualized Education Program (IEP) team determines whether a student needs ESY. Family members participate in the decision. PAVE provides an article: Parent Participation in Special Education Process is a Priority Under Federal Law.
- Services may be provided when school is not normally in session, but not always. Sometimes they are built into the school day. Typically, they are provided during summer. Holiday breaks and after school are options too.
- Parents can keep notes about any loss of skill during a break from school. By tracking how long it takes to recover a skill, parents can provide data for a discussion about whether additional services are necessary.
- ESY are provided at no cost to the family.
Introduction
With summer coming, some parents worry that a child’s progress at school might be erased by the break. Some families may also worry that their child is on the verge of acquiring a new skill and that progress will be disrupted by an extended break. Parents can request a meeting with the Individualized Education Program (IEP) team to review progress and address the concerns. PAVE provides an article with a sample letter to help families request a meeting that isn’t part of the required annual IEP review process.
The team uses existing data and can plan additional evaluations to decide whether the student needs extra instructional time. The student might need supplemental instruction in an academic subject or to maintain a skill in speech/language, occupational therapy, behavior or another area being served through the IEP.
The critical question for the IEP team: Will learning be significantly jeopardized if additional services are not provided?
Extended School Year (ESY) is available for students in special education if there is evidence that without extra instruction they will fall significantly behind in specific skills. Falling behind is formally called regression.
Recovery of skills is called recoupment. A school will provide ESY if regression or likelihood of regression is significant and extra instructional time is needed for recoupment of skills. ESY services help a child maintain skills already being taught and are not provided to teach new skills.
ESY is not the same as summer school
Families often think of ESY as a summer program, but it’s not the same as summer school. A summer-school program might be structured to accommodate a student’s individualized ESY program. ESY and Recovery Services are individualized to serve the needs of a student eligible for special education. The program is structured to fit the student, not the other way around. See PAVE’s video about a student’s right to a Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE): FAPE Fits Like a Proper Outfit.
ESY is usually provided when school is not normally in session, but not always. The IEP team may decide that the services will be most helpful if built into the school day. ESY also can be provided during holiday breaks or as an extension of the typical school day.
Conversations about ESY can happen any time the IEP team meets to discuss progress and goal-setting. If ESY is determined necessary, the IEP document includes an amendment with specific ESY objectives. When an IEP team determines a child eligible for ESY, the school district alerts parents in a Prior Written Notice (PWN) before implementing ESY. If transportation is needed for delivery of ESY services, the district provides transportation.
ESY is not an enrichment program. It is not provided for credit recovery. It is also not a “compensatory service,” which is provided by the district when a student’s services have not met requirements for a Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE).
ESY services might include 1:1 instruction at home, at school or at a district office. A student could also receive ESY as part of “related services” at a provider’s office. (Occupational and speech therapy are examples of related services.) Computer- and home-based learning are additional ESY options. Like all IEP programming, ESY is individualized. Service delivery is designed by the IEP team, and sometimes creative problem-solving is needed.
If the IEP includes ESY services and the family moves during the summer, the new school district is responsible to provide the services as they are designed in the IEP or in a comparable way.
The Washington Administrative Code (WAC) includes information about ESY in sections 392-172A-02020.
How are decisions made about ESY?
The IEP team decides whether a student requires ESY by meeting to review the student’s program goals and progress. PAVE has an article about goal-tracking. Parents or teachers may have notes about any loss of skill during a past break from school.
By making notes about how long it takes to recover a skill after a break, parents can contribute important data. Sharing that information earlier in the school year is ideal, so there is ample time for a review of data and any additional testing. Attendance information also is helpful because some disabilities create illness conditions that keep a child out of school long enough to fall significantly behind.
The school and family discuss whether the lost skills and extra time required to regain them is likely to create a significant barrier to progress toward IEP goals and learning in the future. This will justify whether recoupment is required to reverse or prevent regression. Those are the key words in ESY decision-making.
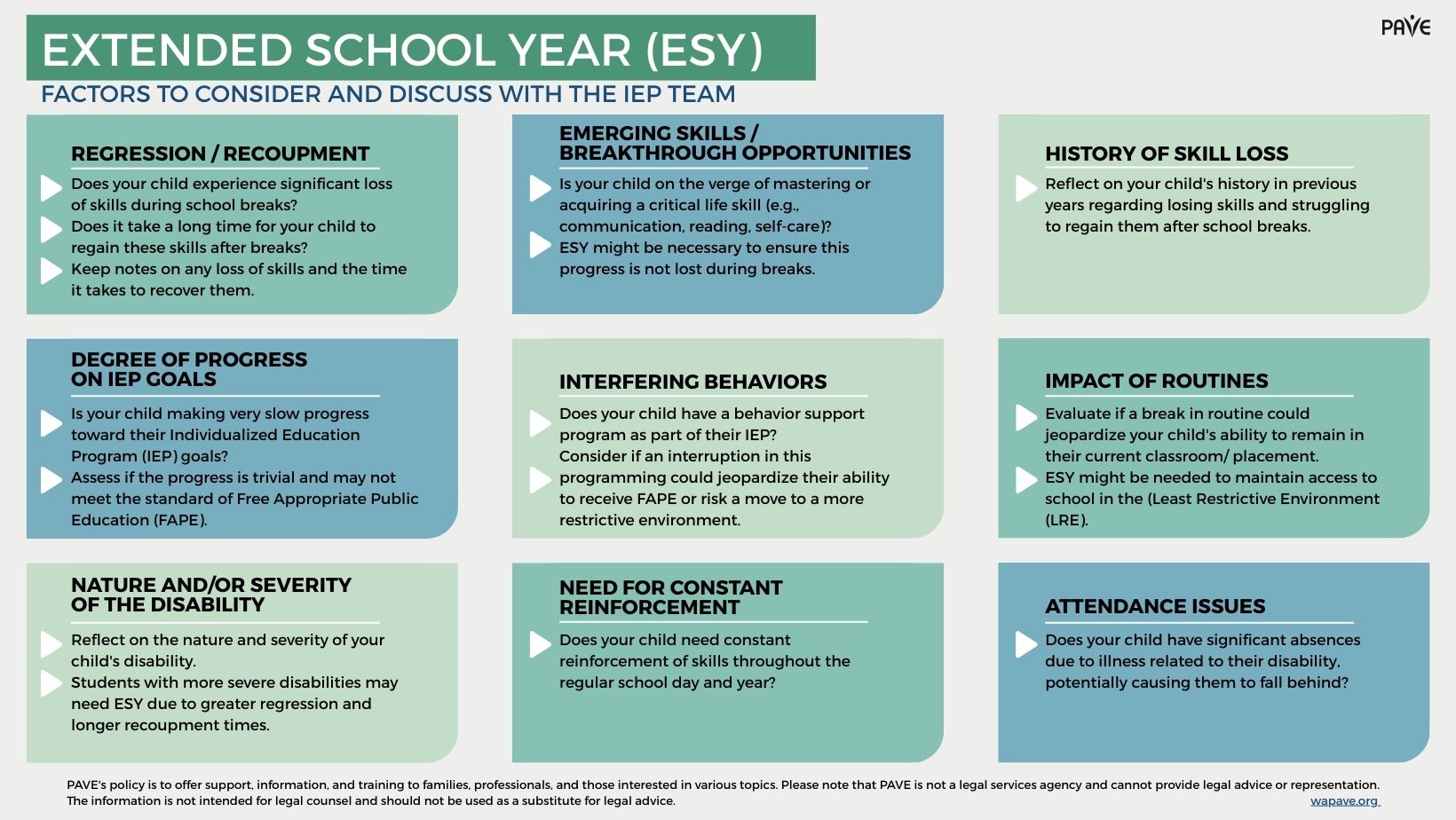
Factors to Consider and Discuss with the IEP Team
Download infographic in English | Chinese (Simplified) 中文 (Zhōngwén) | Korean 한국어 (Hangugeo) | Russian Русский (Russkiy) | Somali Soomaali |
Spanish Español | Tagalog | Vietnamese Tiếng Việt
What does LRE have to do with ESY?
Special Education has Least Restrictive Environment (LRE) as a primary feature. In accordance with the IDEA, a school district is responsible to provide instruction in the least restrictive setting to the maximum extent appropriate.
Accommodations and supports are provided to allow for LRE. Therefore, LRE is part of the school’s obligation to FAPE (Free Appropriate Public Education). For some students, routine is paramount. Parents and teachers can discuss whether a break in routine might jeopardize the student’s ability to remain in their current classroom/placement. If yes, then ESY might be needed for the student to continue accessing school in the Least Restrictive Environment.
What can parents do if they disagree with the school?
Parents who disagree with school decisions have the right to dispute those decisions. PAVE has an article about Procedural Safeguards and dispute resolution options when families and schools disagree. PAVE also provides a video about how to file a Community Complaint, which is one dispute resolution option.
Which students might be eligible for ESY?
ESY is not mandated for all students with disabilities and is not required for the convenience of the school or a parent who might need respite or daycare. There are no federal regulations on ESY eligibility. Some additional considerations may include:
- Regression/Recoupment: Likelihood of regression or anticipating that it will take a long time to get a skill back can make a child eligible for ESY. A student doesn’t have to fully lose a skill or experience a long delay in recovering the skill to qualify.
- Degree of Progress toward IEP Goals: Very slow progress toward IEP goals can meet criteria for ESY. Trivial progress toward goals does not meet the standard of FAPE, as established by a 2017 Supreme Court ruling.
- Nature and/or Severity of Disability: Determination is not limited to a specific category of disability. However, students with more severe disabilities are more likely to be involved in ESY programs because their regression and recoupment time are likely to be greater than students with less severe disabilities.
- Emerging Skills/Breakthrough Opportunities: If a critical life skill is not completely mastered or acquired, ESY services may ensure that the current level of skill is not lost over a break. A few examples of critical life skills include beginning to communicate, learning to read or write, self-care.
- Interfering Behaviors: Some students receive positive behavior support as part of the IEP. When considering ESY, the IEP team would determine whether interruption of such programming would jeopardize the student receiving FAPE.
- Special Circumstances: Sometimes there are special circumstances that prevent a student from learning within the regular school schedule. Districts have different definitions of what constitutes a special circumstance. Parents can ask for a copy of district policy and refer to WAC 392-172A-02020.
No sole factor determines whether a student qualifies for ESY. IEP teams review a variety of data, including informed predictions about what is likely to happen in future based on past experiences. A student who has received ESY in a previous year is not automatically entitled to those services again, and a student who wasn’t eligible in the past is not automatically denied.
In Conclusion
Some students require special education and related services longer than the regular school year in order to receive FAPE. ESY can minimize regression, so a child can catch up or recoup those skills. Parents who have concerns can discuss eligibility criteria with the IEP team. The sooner ESY is discussed, the sooner data can be collected and reviewed. Parent may need time to consider all options and to collaborate with the school.
Learn More
- As part of its Model Forms, the Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) provides a downloadable document that IEP teams can fill out and attach to the IEP when a student qualifies for ESY services. To access the document directly: Extended School Year (ESY) addendum.
- A website called Great Schools.org provides additional information about ESY and downloadable forms about IDEA requirements.
- Wrightslaw.com provides information about the IDEA and legal findings on a variety of topics.

