A Brief Overview:
- Procedural safeguards are a legal requirement for schools and must be provided to parents once a year and during specific situations (e.g., initial referral, filing a complaint, change in placement due to disciplinary action).
- The Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) issued a statewide procedural safeguards notice, available for download in multiple languages, that outlines parental rights in special education.
- The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) requires that each state education agency provide ways to solve disagreements between parents and schools regarding a student’s special education. Procedural safeguards provide information on the formal and informal dispute resolution options available in Washington state.
- Specific protections are in place when disciplining students with disabilities, including requirements for conducting manifestation determinations and continuing education services during extended removals.
- Section 504 includes its own procedural safeguards to protect the rights of students with disabilities who are not eligible for special education under IDEA. The Section 504 Notice of Parent Rights is available for download in multiple languages from OSPI.
Full Article
The Procedural Safeguards are a written set of legal protections under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) designed to ensure that students with special needs receive appropriate education. IDEA, implemented under Washington State law, requires schools to provide the parents/guardians of a student who is eligible for or referred for special education with a notice containing a full explanation of the rights available to them (WAC 392-172A-05015). Understanding these safeguards allows for effective advocacy in a child’s education and ensures their rights are protected throughout the special education process. They do not constitute legal representation or legal advice.
A copy of the procedural safeguards notice is downloadable in multiple languages from the Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI). School districts must provide this notice once a year and during key times such as:
- At the initial referral for special education evaluation and at least once every year after.
- Upon receipt of the first special education complaint or due process hearing request filed by a parent or guardian in a school year.
- When a school decides to remove a student for more than 10 school days in a year through exclusionary discipline, and that removal constitutes a change in placement.
- Any time a parent, guardian, or student aged 18 or older requests them.
In addition to detailing when the procedural safeguards notice must be provided, the procedural safeguards contain information about several key areas, including:
Prior Written Notice
Schools must give prior written notice (PWN) before making any significant decisions about a student’s education, such as changes in identification, evaluation, or placement. This notice must include a detailed explanation of the decision and the reasons behind it. This document is shared after a decision is made and prior to changes in a student’s educational program.
Parental Consent
Schools must get written parental consent (permission) before conducting an initial evaluation or providing special education services for the first time. Parents can withdraw their consent at any time, but this doesn’t undo actions already taken. Once consent is given, the school has 35 school days to complete the evaluation. This consent is only for the evaluation, not for starting services. If the child is a ward of the state, consent might not be needed under certain conditions. When starting special education services under the initial IEP, the school must get consent again, and if refused, they can’t force it through mediation or legal action. Consent is also needed for reevaluations involving new tests, and schools must document their attempts to get it. However, consent isn’t needed to review existing data or give standard tests that all students take.
Independent Educational Evaluation
If a parent disagrees with the school’s evaluation of their child, they can ask for an independent educational evaluation (IEE) that the school district will pay for. The district must give the parent information on where to get an IEE and the rules it must follow. If the district does not agree to the IEE, they have 15 calendar days to either start a file a due process hearing request or agree to pay for the IEE. PAVE provides a downloadable sample Letter to Request an Independent Educational Evaluation.
Confidentiality of Information
Student educational records are confidential. IDEA provides parents and guardians the right to inspect and review their student’s educational records and request amendments if they believe they are inaccurate or misleading. When the child turns 18 years of age, these rights pass from the parent or guardian to the student. The Department of Education provides a website page called Protecting Student Privacy to share resources and technical assistance on topics related to the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA). The procedural safeguards explain terms about educational records from IDEA and FERPA to help parents understand their rights and protections.
Dispute Resolution
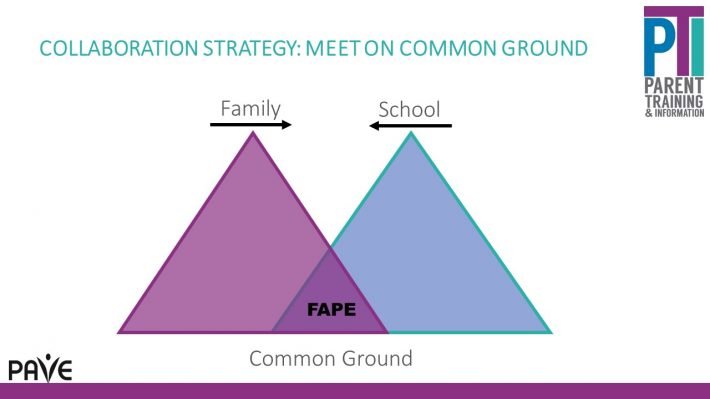
IDEA requires that each state education agency provide ways to solve disagreements between parents and schools regarding a student’s Individualized Education Program (IEP). In Washington State, there are both informal and formal options. When parents and school districts are unable to work through disagreements, the procedural safeguards outline the dispute resolution processes available. These options ensure that parents and schools can work towards a mutually agreeable solution while protecting the child’s right to a Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE). The formal dispute resolution options available through OSPI are mediation, due process hearings, and state complaints.
Disciplinary Protections
When disciplining students eligible for special education, schools must follow specific rules to ensure fair treatment. If a student is removed for more than 10 consecutive school days or shows a pattern of removals totaling over 10 days in a school year, it’s considered a change of placement, and parents must be notified. After 10 days, the school must provide services to help the student continue their education. A manifestation determination must be conducted within 10 days to see if the behavior was related to the student’s disability. If it was, the IEP team must address the behavior and return the student to their original placement unless agreed otherwise. If not, the student can be disciplined like other students but must still receive educational services.
Also, schools must keep providing educational services to students with disabilities even if they are removed from their current school setting for disciplinary reasons. This helps the student keep making progress in their education. Parents and guardians have the right to join meetings about their child’s disciplinary actions and can ask for a due process hearing if they disagree with decisions. These safeguards ensure students with disabilities receive necessary support and fair treatment during disciplinary actions.
In special cases, such as carrying a weapon or using drugs at school, the student can be placed in an alternative setting for up to 45 days regardless of whether the behavior was related to the student’s disability.
Protections for Students Not Yet Eligible for Special Education
The procedural safeguards outline protections for students who have not yet been found eligible for special education but for whom the school should have known needed services. A school is considered to have this knowledge if a parent previously expressed concerns in writing, requested an evaluation, or if staff raised concerns about the student’s behavior to supervisory personnel. However, if the parent refused an evaluation or the child was evaluated and found ineligible, the school is not considered to have knowledge. In these cases, the student may be disciplined like other students, but if an evaluation is requested during this period, it must be expedited. If the student is found eligible, special education services must be provided.
Requirements for Placement in Private Schools
If parents believe the public school cannot provide FAPE and choose to place their child in a private school, there are steps to request reimbursement from the district. If the child previously received special education services, a court or administrative law judge (ALJ) may require the district to reimburse the cost of private school enrollment if it is determined that the district did not timely provide FAPE and that the private placement is appropriate, even if it does not meet state educational standards.
Reimbursement may be reduced or denied if the parent did not inform the IEP team of their rejection of the proposed placement during the most recent IEP meeting, failed to provide written notice to the district at least 10 business days before the removal, or did not make the child available for a district evaluation after prior written notice. However, reimbursement cannot be denied if the district prevented the notice or if the parent was unaware of their responsibility to provide it. The court or ALJ may also choose not to reduce reimbursement if the parents are not able to read or write in English, or if reducing or denying the reimbursement would cause serious emotional harm to the child.
This PAVE article, Navigating Special Education in Private School, explains the rights of students to receive equitable services in private schools, regardless of whether they are placed there by their parents or through an Individualized Education Program (IEP) decision.
Procedural Safeguards under Section 504
The procedural safeguards under Section 504 ensure that parents are informed of their rights before any evaluation or development of a 504 plan begins. These safeguards include the right to request a referral for evaluation, the formation of a 504 team to assess the student’s needs, and the requirement for parental consent before any evaluation or implementation of the plan. Parents must be provided with a copy of their rights at key points in the process. Additionally, the school must review and evaluate the 504 plan annually and re-evaluate the student’s eligibility at least every three years. Parents also have the right to file formal complaints if they believe the school is not following the 504 plan or if their child is experiencing discrimination or harassment. The Section 504 Notice of Parent Rights is available for download in multiple languages from OSPI.
Conclusion
Procedural safeguards are a requirement under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) that ensure the rights of students with disabilities and their parents are protected throughout the special education process. By outlining the legal protections available, these safeguards empower parents to actively participate in their child’s educational planning and decision-making. Understanding these rights—from prior written notice and parental consent to confidentiality and dispute resolution—allows families to advocate effectively and collaborate with schools. Through adherence to these safeguards, schools and parents can work together to provide a Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) tailored to the unique needs of each child.
Additional Resources:
- OSPI’s Special Education webpage includes information about data collection, dispute resolution, funding information, guidance for families, legal procedures, program improvement initiatives, resource libraries, and support for secondary transition services.
- Special Education Parent & Community Liaison provides non-legal support by phone (360-725-6075) or through an online message portal, Ask OSPI web page.
- PAVE provides direct support to parents and guardians, youth with disabilities, adult self-advocates, and professionals. Complete the Get Help request form to be connected with individualized information, resources, and training.