Families may feel uncertain or discouraged when a school denies a request for special education evaluation or finds a student ineligible for services. Fortunately, there are steps families can take to respond, seek clarification, and continue advocating for their child’s needs. Understanding available options and protections can help families take informed action and make decisions that support their child’s access to appropriate educational services.
A Brief Overview
- If the school denies a request for a special education evaluation or does an evaluation and determines a student is ineligible for services, families have options.
- Schools must issue a Prior Written Notice (PWN) explaining their decision to evaluate or deny a request.
- Students who do not qualify for an IEP may still be eligible for a Section 504 Plan.
- Procedural Safeguards provide a specific process for special education and offer families the right to file formal complaints when they disagree with school decisions.
- When there is a dispute about a district’s evaluation, one option is to request an Independent Educational Evaluation (IEE) from a provider outside of the school district. This article includes a downloadable sample letter in multiple languages to help with that process.
- PAVE supports students and families navigating educational services. Click Get Support at wapave.org to request 1:1 support.
Introduction
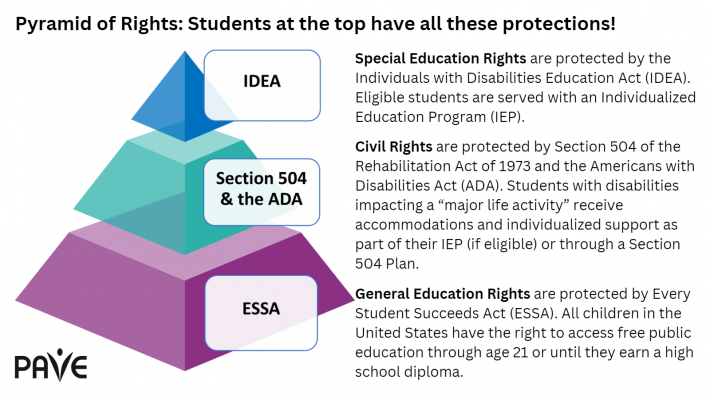
Parents have a variety of choices if the school denies a request to evaluate a student for special education, or if the school does an evaluation and finds the student ineligible for services through an Individualized Education Program (IEP). These decisions can feel discouraging, but they do not mark the end of the road. Under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and its implementation through Washington Administrative Code (WAC 392-172A), families have the right to challenge decisions, seek clarification, and request further evaluation. Understanding these options can help families take informed next steps and ensure that their concerns are heard and addressed.
Ask for the Decision in Writing
The school is required to respond through a formal letter, called Prior Written Notice (PWN), to explain its rationale for moving forward with an evaluation or denying the request. If the explanation is unclear or lacks detail, families can ask for a more complete written response. Schools may not deny an evaluation based on internal resource limitations or staffing challenges. According to the Child Find Mandate of IDEA, schools are obligated to evaluate any student with a known or suspected disability, regardless of whether other classroom supports are being used. For example, schools may implement approaches like Response to Intervention (RTI) to support learning, but these methods cannot be used to postpone or deny assessment when a disability is suspected.
Request a Meeting
Discussing a student’s difficulties in a meeting, in-person or virtually, can help school staff understand a parent’s level of concern. A district representative, such as a director of special education, can provide insight about the process and additional options. Parents can invite anyone they would like to attend who has knowledge of the student, including a support person to take notes and help track the conversation.
Is a Section 504 Plan Appropriate?
If a student has a known disability, with some educational impacts, but there is no documented need for Specially Designed Instruction (SDI) and/or related services, the student might qualify for accommodations provided through a Section 504 Plan.
Section 504, which is part of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, defines disability as an impairment that impacts a major life activity. A formal evaluation is helpful but not required, and parent involvement is best practice. The team asks:
- Does the student have a disability?
- Does the disability limit one or more major life activities?
If the answer to these two questions is yes, the school can develop a plan to support the student within the general education setting. Assistive technology and modifications to the curriculum can be part of the plan, which includes individualized accommodations to ensure the student is able to access school in ways that are equitable. PAVE provides an article with more information about Section 504.
Options When Resolution Requires More Support
Families are protected by Procedural Safeguards, which outline a specific processes for resolving disagreements in special education. When informal conversations don’t lead to resolution, options such as mediation, community complaint, and due process may be appropriate. PAVE’s article, When Parents and Schools Disagree: Navigating Special Education Disputes, offers clear guidance on these pathways and what to expect.
If a school denies a request for a specific evaluation, such as a Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA) or an assistive technology evaluation, families can still pursue dispute resolution options. These types of assessments may be essential for understanding a student’s behavioral needs or identifying tools that support access to learning. Requests for these evaluations are protected under the same legal framework as other special education decisions, specifically the procedural safeguards.
The Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) provides assistance to navigate these processes through a Special Education Parent Liaison, and families may also seek help from the Governor’s Office of the Education Ombuds for collaborative problem-solving. For personalized assistance, PAVE supports students with disabilities and their families. Click Get Support at wapave.org to request 1:1 support.
Request an Independent Education Evaluation (IEE)
Families who disagree with a school district’s evaluation results have the right to request an Independent Educational Evaluation (IEE) conducted by a qualified professional outside the district. An IEE can offer additional information that may support the need for Specially Designed Instruction (SDI) and/or related services.
If the school district denies a request for an IEE at public expense, the district must initiate a due process hearing within 15 calendar days to show that its evaluation was appropriate.
When an IEE request is accepted, the school district provides a list of independent evaluators. Parents have discretion to call each one or to seek an alternative evaluator at their own expense before choosing who will evaluate the student. The school must consider the results of the IEE when deciding whether the student qualifies for special education programming.
Sample Letter to Request an IEE
Download the Sample Letter to Request a Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA) in:
English | Chinese (Simplified) 中文 (Zhōngwén) | Korean 한국어 (Hangugeo) | Russian Русский (Russkiy) | Somali Soomaali | Spanish Español | Tagalog | Ukrainian українська | Vietnamese Tiếng Việt
Families can email the IEE request letter, send it by certified mail (and keep the receipt), or hand carry it to the district office and request a date/time receipt. It is important to keep a copy of this letter and all school-related correspondence in the student’s home records. Organizing with a binder or a filing system helps with keeping track of all letters, meetings, conversations, etc. These documents will be important for student throughout their educational career and beyond, including when they transition out of school.
Final Thoughts
When a school says “no,” it can feel like a door has closed—but that moment can also mark the beginning of a more empowered path forward. Each action a family takes is a meaningful expression of care and commitment. Family caregivers should trust their instincts, lean on trusted resources, and reach out for support. Persistence paired with informed choices can lead to real change and this journey is about more than advocacy—it’s about championing a child’s right to thrive.
Learn More
- PAVE – Evaluations Part 1: Where to Start When a Student Needs Special Help at School: Understand the initial steps in the evaluation process, including eligibility criteria and how to prepare for an IEP.
- PAVE – Where to Begin When A Student Needs Help: A comprehensive toolkit offering sample letters, timelines, and guidance for families just starting the special education journey.
- OSPI – How Special Education Works: A 10-step guide to understanding the special education process from referral to transition planning.