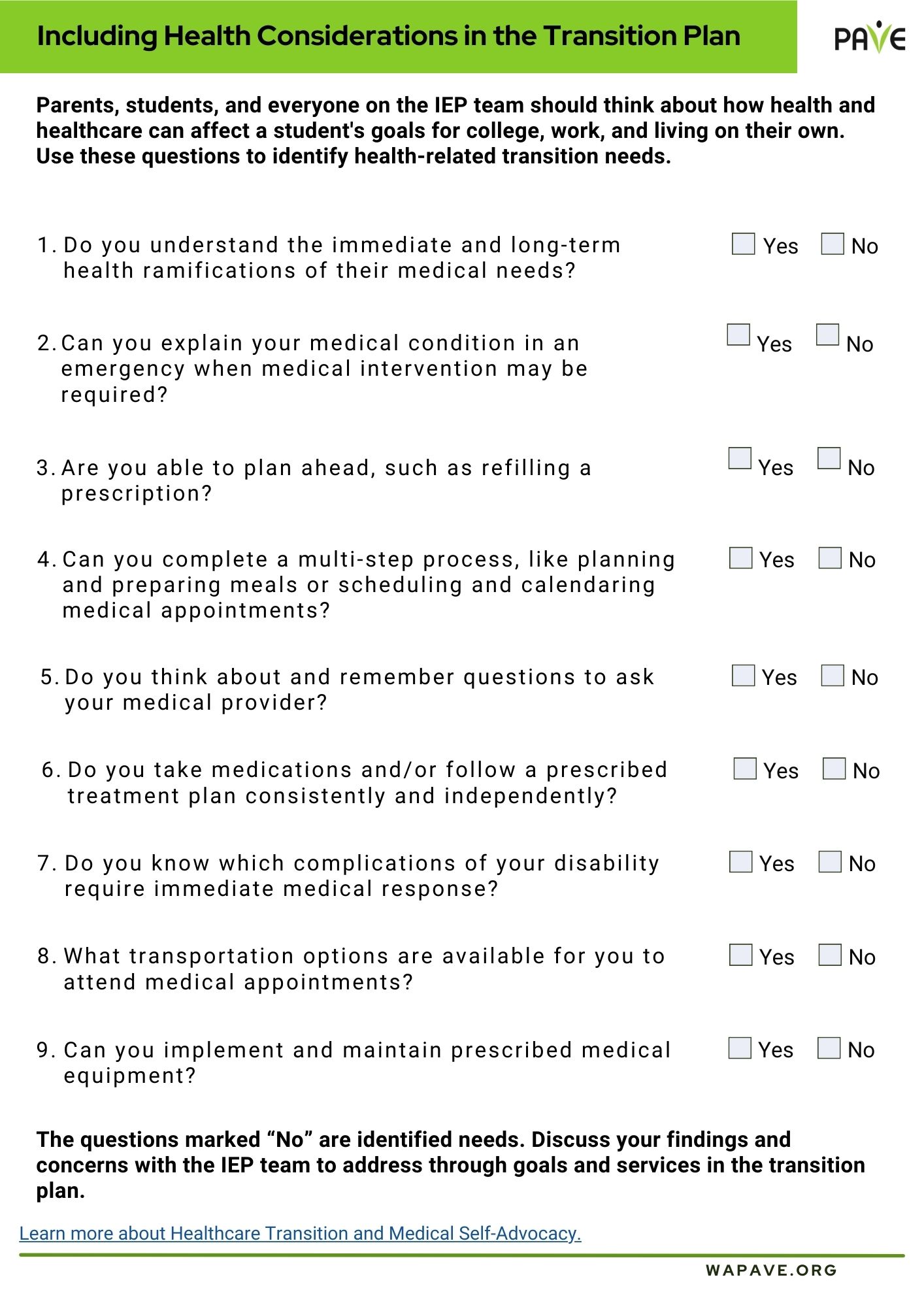
Every family experiences holidays and end-of-year transitions differently. This article provides a sampling of ideas for families with children (of any age) experiencing special healthcare needs or disability. If a child also experiences behavioral difficulties, you may wish to read Home for the Holidays: The Gift of Positive Behavior Support
A Brief Overview
Here are some quick takeaways:
- Keep to your everyday schedule and routine as much as possible to minimize medical and behavioral impacts.
- Add fun with home-based holiday activities and traditions tailored to your family’s needs or select family or group activities which work with your child’s medical needs.
- Plan and save surprises too: Mix up the activities so children can help with some planning and enjoy a few surprises.
- Plan for health and safety if travel is on the schedule.
- The article includes suggestions for parents and other family caregivers to help support you as a family caregiver during the busy holiday season. Includes ideas for parents in the “sandwich generation”.
- Gratitude is a gift: Moments of thankfulness calm the mind. For additional stress-reducers, PAVE has a practical gift: Self-Care Videos for Families Series. We also offer short videos to help everyone find calm (Try Hot Chocolate Breath!): Mindfulness Video Series.
Get Holiday Help
Parents and family members who care for an individual with special health care needs or a disability are already busier than most people. It’s very common for a primary caregiver, the person usually caring for a person with health needs or disability, to believe that all the extra planning for holiday time is their responsibility, too.
This season, use these reminders and tips to help yourself as a parent or other family caregiver to some holiday spirit:
Share your holiday wish list with extended family and friends. Here are some ideas:
- Ask for time off from caregiving duties as a gift for the holidays (respite). Can another family member, extended family member, or friend take over some caregiving tasks? Perhaps they could pay, or help you pay for a home care worker or a stay at a respite facility.
- Can a family member or friend help with chores, household maintenance, holiday cleaning, shopping, decorating? Look at your household’s to-do list and just ask.
- Childcare when school’s out: “You know, for Channukah this year, I’d love it if you could come over and play with the younger kids while I do XYZ”.
- Gift certificates for relaxing /pampering activities are great too: spa time, for example!
Order in holiday-time meals or ask for the pre-holiday gift of donations of baked goods, meals you can freeze/reheat, or gift cards to food delivery services from restaurants or supermarkets.
Money: Make a holiday spending budget with your spouse or partner to reduce financial stress. Ask extended family members to agree on a dollar limit for gifts and/or set up a gift exchange where names are drawn.
Are you a “sandwich generation” caregiver, caring for both children and older family members with health or other conditions? Carol Bradley Bursack, writing on Aging Care, shares this insight:
“The squeeze of generations and the countless needs of each leave little time for caregivers to think of their own needs. Members of the sandwich generation know this dilemma well. Prioritizing our own health and enjoyment winds up feeling like just another task, so we knock it to the bottom of the to-do list and keep on doing for everyone else…
Communicate with your loved ones. Even small children can understand—if they are told in a loving way—that your time is short or you have to cut corners because Grandma and other family members rely on you, too. Communicate the same thing to the elder(s) in your care. Helping the entire family understand that each person’s desires are important to you but that you have a lot on your plate can help keep their expectations more realistic. You’d be surprised how much a senior, even one who has dementia, can understand.”
Learn more about the difficult choices facing “sandwich generation” family caregivers in another article by Carol Bradley Bursack, A Story from the Sandwich Generation: Caring for Kids and Parents1
Decide Which Routines and Schedules Might Be “Holiday Flexible”
“Many children with disabilities rely on schedules, either as a coping strategy or for medical reasons. It is critical to keep your child on schedule during the holidays as much as possible. This may mean leaving an event early or arriving later to accommodate tube feedings or respiratory treatments. It may mean putting your child to bed on time, even at Aunt Sally’s midnight party.” -Susan Agrawal, complexchild.org . A “reason” for leaving an event might make it easier for a child to leave an event when others are staying. “It’s time for us to get the food ready for Santa’s reindeer” or “let’s head home for a special holiday treat” may help get everyone out the door!
If your family can accommodate a bit more flexibility, a “Holiday” sleep schedule with an extra hour of special family time before bed might add a fun holiday flavor. For others, sleeping in or staying in jammies longer than usual might create a relaxing holiday feel. Be sure to call out these relaxed rules as holiday specials so everyone understands they are temporary changes and part of the “break.”
Keeping to a schedule and getting regular physical exercise and good sleep is important for everyone else in the family, too!
Set Expectations with Extended Family
No holiday is ever perfect, and unrealistic expectations can cause a celebration to sour. Communicating with relatives and friends can help:
- Make a “Gift Wish List” for your child with special healthcare needs to let relatives and friends know what gifts will be good for your child based on what they might need to avoid and what they can use and enjoy. Many large retailers (Target and Kohls, for example) carry lines of adaptive clothing and sensory products and toys.
- Ask for understanding and support from family and friends to reinforce positive messages and realistic expectations. Saying no might be important, so choose what works and toss the guilt if the family needs to pass on a tradition or an invitation. Or use the “No, but” strategy and offer an alternative such as a different time or activity, or a virtual get-together.
Travel
For families choosing to travel, bags with medication and equipment still need to include masks, hand sanitizer, and sanitizing wipes. Even with mask mandates mostly a thing of the past, it’s sensible to have these on hand for crowded airports and planes and visiting more vulnerable, elderly relatives.
If plans include planes and trains, be sure to let agents and attendants know about a family member’s special accommodation needs.
- Washington travelers can make preflight preparations from Sea-Tac Airport by sending an email to the Sea-Tac Airport customer service.
- The phone number for the Spokane Airport Administrative Offices: (509) 455-6455. Amtrak provides a range of Accessible Travel Services.
- TSA Cares is designed to aid travelers with disabilities with TSA screening procedures. Call them at 855-787-2227 (8 AM to 11 PM Eastern Time M-F, and 9 AM-8 PM Eastern weekends and holidays).
Sugary treats might impact planning for children with diabetes: An insulin pump might help during the temporary splurges so a child can enjoy the holiday without feeling too different or overwhelmed.
- Visions of sugar plums might need a different flavor for children with specific allergies or food sensitivities. Being prepared with substitutions may prevent a child from feeling left out. If someone else is doing the cooking, be sure to share about any severe allergies to make sure utensils and mixing containers do not get cross-contaminated.
Add Fun
ASK your family-what do they like best about a holiday? (Christmas, Channukah, Kwanzaa, Diwali, Eid al-Fitr, etc.) Keep these wishes in mind when you select and plan for holiday activities. This may help you to keep your to-do list focused on what your family looks forward to, or would like to change, rather than an overwhelming set of holiday “to-dos”.
Give the gift of Giving. Every person deserves the chance to be of help to others and make them feel loved. Small children, children with special health conditions, children of any age with intellectual disabilities, children with developmental disabilities can participate in the act of giving holiday gifts. It’s a great way to boost a person’s capabilities and sense of belonging.
Making home-made holiday cards, simple handcrafted items, baked goods, or purchased inexpensive items from a dollar store can be great holiday family activities or a chance to spend one-to-one time with an individual child.
Families can set aside time for, or add on to ordinary routines, time for reading special holiday stories, playing games, or watching silly holiday movies. Laughter is therapeutic!
Understanding your child’s healthcare needs and vulnerabilities can help with deciding which activities are right for your family. It’s also important to think about which activities will help you, the caregiving parent or family member, recharge—and which ones to prioritize in terms of time and energy.
- Drive-through light shows, streaming concerts, theater, and holiday events are options in some areas that won’t expose a medically vulnerable child to other people’s germs.
- If weather and your family’s needs permit, outdoor holiday activities with groups of people are less likely to spread illness, as we all learned during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. Think of tree lightings, caroling, snow-sculpture or snowman-making events, and of course winter sports, if appropriate, for your child and family.
- One tradition that has always been virtual is the NORAD Santa tracker, which keeps tabs on Santa’s travel on Christmas Eve and has kid-centered games and songs.
Finding the “just-right” amount of holiday celebrating can be tricky, so keep the Three Bears/Goldilocks principle in mind. For children who understand this theme, families can use the classic story to talk about how everyone makes choices about what is the “just right” amount of celebrating, eating, screen time, sleeping.
Plan and Save Surprises Too
A theme for the year can add a new flavor to family traditions. Here are some suggested themes:
- How I celebrated when I was a kid.
- Christmas 1821, 1721, etc.
- Holiday food, decorations, stories, music, etc. from another culture.
The family can research the theme together to come up with ideas and activities. A theme night might include a chance for each family member to share something or lead an activity. On story night, each person might share a favorite holiday memory or a made-up story. If extended family want to take part, a video conference might be an added element to the evening.
Adults can set aside a few ideas to save for in-the-moment surprises to sprinkle in. A prize, special treat, well-told joke, customized family game, or a surprise “guest” on the phone are a few ideas to plan out in advance.
Gratitude is a Gift
Gratitude helps the mind escape from stress-thinking and move toward feelings of peacefulness and grace. Taking a few moments to mindfully reflect on something that brings joy, beauty, love, sweetness—anything that feels positive—can create a sense of ease.
For additional stress-reducers, PAVE provides a practical gift: Self-Care Videos for Families Series. We also offer short videos to help everyone find calm (Try Hot Chocolate Breath!): Mindfulness Video Series.
Susan Agrawal, writing on complexchild.org, reminds us “No holiday is ever going to turn out like you want it to, even if you have the most perfect storybook family in existence. Don’t expect perfection or anything even close to perfection. For some families, getting through the holidays may be as much as you can expect. For other families, changing holiday traditions may make the season not feel the same. That’s OK. Instead, try to find the blessings in the season, whether that means seeing family members or celebrating your child’s inch stones.”
Additional Holiday Resources
PAVE:
- Giving the Gift of Sensory-Regulation: Supporting a Happy Holiday Season for All
- Home for the Holidays: The Gift of Positive Behavior Support
Neurodivergence and the holidays: Creating Joyful and Inclusive Holidays 4-Part Series:
- Supporting a Neurodivergent Family Member During the Holidays
- Creating Joyful and Inclusive Holidays: Sensory Friendly Tips for Neurodivergent Loved Ones
- Creating Joyful and Inclusive Holidays: Meeting Neurodivergent Needs While Traveling
- Creating Joyful and Inclusive Holidays: Comfortable Social Spaces for Neurodivergent Individuals During the Holidays
Aging Care:
- Caregiving During the Holidays: Have a Realistic, Positive Approach
- A Story from the Sandwich Generation: Caring for Kids and Parents
Complex Child: